Sharding in MongoDB
Sharding, can also be called horizontal scaling. The scaling approach divides the data set and distributes the data over multiple servers. Each of this server can be called a shard. Each shard is an independent database, and collectively, the shards make up a single logical database.
###What other components are required for MongoDB sharding?
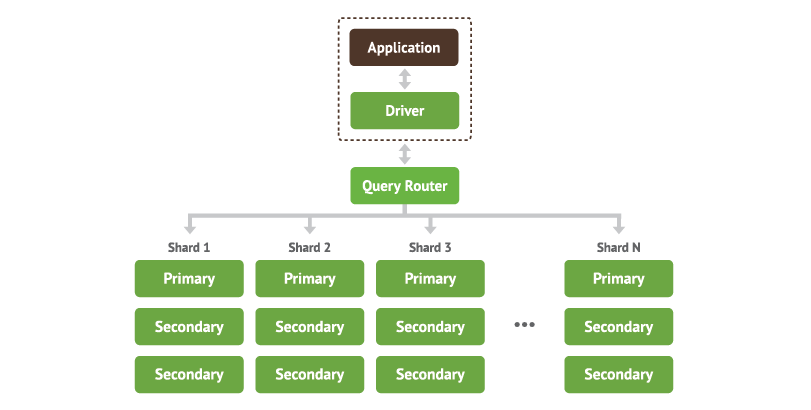
Like mentioned above, the Shards stores the data. For ensuring that shards are highly available, you need to have replica sets . We will go into more details later around replica sets, but for now the easiest way to explain this is - you could have a primary shard which you can write to and a second shard which is paired with the primary shard hosting the same data which you can read from. When you do sharding, you would need to know which shard to get the data from. This is done by the Query Router. The Query Router direct requests to the appropriate shard or shards. It processes and targets operations to shards and then returns results to the clients.
###How does the query router know which shard to get the data from ? This information is stored in Config servers. They store the cluster’s metadata. This data contains a mapping of the cluster’s data set to the shards. The query router uses this data to route requests to the right shards.
